Start Early Washington is fortunate to work with committed partners like Perigee Fund who believe in the power of healthy relationships with caregivers to give babies and toddlers the best start in life. Learn more about how Perigee Fund prioritizes investment in infant and maternal mental health in our recent conversation with Perigee team members Becca Graves and Kim Gilsdorf.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive the latest early learning program and policy news in Washington state.

Looking for Bright Spots
What are some of the biggest things you’ve learned in supporting infant and maternal mental health?
Becca: I have been really impressed by the leaders that we have encountered in Washington State and across the United States. We all know there are not enough resources in the ecosystem to support families. We also know there is not enough support for the work that infant and maternal mental health leaders are doing. Yet so many leaders are willing to step forward with partners and make things happen. For example, Perinatal Support Washington and Start Early partnered to provide home visitors with Maternal Mental Health training. That partnership has created new mental health resources for the workforce and for families.

Kim: Because early childhood and parent mental health is so under-resourced, there are opportunities for progress in many kinds of systems. That is helpful because as we seek to fund systems change, we can remember we don’t have the answers. We can’t foresee which groups of stakeholders, in which systems, are going to rise to the occasion because they care deeply about the bond between caregivers and a child, and they see how important that is to their work.
In Tennessee we see leadership from community behavioral health, in California we see innovation led by pediatricians and community health workers, and in New Jersey there are doulas growing access to maternal mental health care. These examples are the tip of the iceberg. The diversity of ways to make progress is both a lesson learned as well as an approach we can continue to support.
Creating a Movement
(Start Early) Are you finding new champions for infant and maternal mental health emerging since Perigee began in 2018?
Becca: We have learned that there are champions everywhere. I think our mission calls us to learn about opportunities to help everyone see the importance of child and family wellbeing and valuing the earliest relationships. Particularly where there are instances of trauma in a family’s experience, either now or intergenerationally.
Whether it’s guaranteed basic income or child welfare, there are people in tune with needs and opportunities, and there are people who are curious and want to learn more. By gathering people together, getting to know one another, and talking about the issues, you can see the places where the family economic security goals and the mental health goals can come together and be in alignment.
When parents experience adversity, such as poverty, trauma and racism, their children can feel lasting effects, even into adulthood. Early support for babies, families, and caregivers can lessen the impact, leading to better long-term health and well-being.
Perigee Fund
Building for the Future
What would the biggest impact or change you would like to see over the next 10-15 years because of Perigee’s intentional investments?
Kim: I’d like to see policy makers have a greater understanding of the fundamental importance of early relationships. That mental model shift is part of creating policies that make mental health support more equitable and more accessible for families with very young children.
Becca: We need to value and embed support for families in the places where they are. Certainly, there are many ways that families support themselves and communities support families that don’t require additional resourcing, but they do require us to respect and value the importance of family relationships and community relationships and not get in the way. And there is a lot that we should be doing differently with our public policy and with the ways that we think about community-based models of care.
Supporting the Field
This is hard work and it’s not as easily measured as “can your child read by third grade.” Perigee has been such a champion in helping to advance our Neuroscience, Epigenetics, Adverse Childhood Experiences, Resilience (NEAR@Home) trauma-informed training to support home visitors in building a hope-focused approach when talking with families about trauma. It is also some of the most promising work we have for infant and maternal mental health. Can you tell us about why you chose to support NEAR?
Kim: NEAR does something with grace that is both important and difficult. It helps families and providers navigate difficult conversations about trauma, slowly and with compassion. Conversations about early childhood trauma can be very challenging for all involved, which is part of why many infant mental health professionals are invested in ongoing learning and reflective supervision. NEAR makes it possible to integrate some of that skill building and support into the job of being a home visitor. Regardless of their degree or education, all home visiting professionals trained in NEAR get the support they need to navigate hard topics with families and to do so with kindness and love. It is incredible!
Learn more about Perigee Fund’s priorities for Infant and Early Childhood Mental Health.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive the latest early learning program and policy news in Washington state.
As a former preschool teacher, Adrienne Matthias, Start Early Washington Home Visiting Training Manager has always believed in the power of early connections with families. While teaching in Korea in her twenties, she recognized that the most powerful way to reach children was through the parents and caregivers who really had the strongest relationship with them. This awareness of the opportunities to create healthy relationships early on is what eventually led her to home visiting.
Planting the Seeds for Early Intervention
Back in the U.S. teaching preschool, the idea of connecting with families as early as possible became more important to Adrienne, strengthening her view that all parents need support during those first critical years of a child’s life. This led Adrienne to training as a home visitor, because as she sees it, home visiting provides an important resource, partnering with parents in ways that differ from a traditional classroom setting. Home visitors can support parents, building their confidence and providing tools and emotional support during the critical early days of parenting.
It’s not just about watching this child develop, it’s about watching the parent develop and step into their parenting with the knowledge to be able to advocate for their children and see themselves as good, worthy parents.
Adrienne Matthias, Start Early Washington Home Visiting Training Manager
A Journey to Infant and Toddler Mental Health
As she became a program manager, Adrienne found new meaning in working with home visitors and parent educators through reflective supervision, making time for them to slow down and think more deeply about their practice. By shifting the focus to the home visitor and their needs, it could have significant impact on the delivery of services to families. Adrienne felt a growing desire to learn learning more about infant and toddler mental health, which led her to the Infant Toddler Mental Health certificate program and Portland State University’s Early Childhood Inclusive Education Master’s Degree. Drawn in by the school’s strengths-based and collaborative approach, and infant mental health classes’ exploration of the dynamic between parent-child or caregiver-child relationship in particular, the program reinforced her beliefs of how these interactions profoundly shape a child’s development while impacting the parent’s journey. One that Adrienne sees as a delicate dance that requires understanding, empathy, and advocacy.
The Dance of Parenting
As Adrienne shared, mothers, in particular, often struggle with self-doubt when it comes to parenting. “We tend to focus on our perceived shortcomings rather than celebrating our strengths. Home visiting that supports infant and maternal mental health can step in to bridge this gap. By supporting parents, we empower them to build strong attachment relationships. It’s not just about the child’s growth it’s about the parents’ growth too, and as home visitors, we can be a part of facilitating this transformation firsthand.”
Unseen Impact
Home visitors rarely know the full impact of their work. However, home visitors all have stories that demonstrate the power of the program to support families. Adrienne shares one story of a distressed mother who truly believed she couldn’t handle parenting. Her daughter’s tantrum at a bouncy house left her feeling inadequate and unequipped. By exploring the mother’s strengths, emphasizing and reminding her of the effort she put into creating enriching experiences for her child, despite the challenges of the moment, she was able to recognize that she had persevered through the challenge, and she was able to do it because she knew it was beneficial for her child. Leaning into the strengths-based aspects of the interaction and being able to normalize these emotional moments helps parents recognize their worth.
There are hard things all the time, and it doesn’t mean that you ignore them. The strengths-based approach is how you humanize them and how you hold people in your mind, how you treat people because you are holding them fully as people. That is the most important thing to remember.
Adrienne Matthias, Start Early Washington Home Visiting Training Manager
The Luxury of Strengths-Based Approaches
In trauma-informed principles, like those at the center of the hope-filled, compassionate NEAR@Home practice for addressing childhood trauma, being strengths-based is essential. Imagine entering someone’s home and focusing on what they’re doing well instead of pointing out flaws. It’s a necessity to be able to see what is going right —one that reveals genuine strengths. When home visitors are able to help parents see the best in themselves, we empower them. It’s not about rigid rules; it’s about acknowledging their efforts. Even after tough experiences, it’s critical to be able to take a step back and appreciate the positives—a parallel process that enriches the practice.
Continuing to Emphasize the Positive
Maternal and infant mental health isn’t just about fixing problems; it’s about celebrating strengths. Home visitors hold a unique position—to witness growth, resilience, and love within families. As Adrienne continues in her role leading Washington’s training efforts and expansion of NEAR trauma-informed practice, she believes in the power and potential of these strengths-based approaches to empower families to build strong and healthy relationships that will last a lifetime.
The mental health of parents plays an important role in shaping the trajectory of their child’s social and emotional well-being.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
We asked Michael Gouterman, our mental health expert, why prioritizing parental mental health is essential for nurturing a healthy environment for children to thrive.
- Understanding the Impact
Parents are their children’s first teachers, and it is the quality of parent-child relationships and interactions that create the foundational skills that children need to be successful in school and in life. When parents experience mental health challenges, it can have ripple effects on their children’s development. - The Dysregulated World
Imagine a child born into a world where their caregivers are grappling with their own dysregulation—an environment marked by stress, anxiety or depression. In such circumstances, the ability of caregivers to provide consistent emotional support and regulation may be compromised, impacting the child’s sense of safety and security. Read our tackling tough topics posts on: Racism and Violence - The Transmission of Stress
Stress has a way of affecting parent-child relationships and impacting the way children may perceive the world. When parents struggle with their mental health, children may internalize this stress, leading to challenges in emotional regulation and social and emotional development. - Empowering Parents as Advocates
Recognizing the importance of parental mental health is not about assigning blame, but rather acknowledging the complex interplay between individual well-being and environmental factors. Empowering parents to advocate for their own mental health is paramount, ensuring they have access to resources and support systems to address their needs. - Breaking the Cycle
When we prioritize parental mental health, we can break the cycle of the intergenerational transmission of stress and help create an environment where children can thrive. When parents prioritize their own well-being, and are better equipped to provide the support and stability their children need to navigate life’s challenges.
Helpful Mental Health Resources for Parents
- Mental Health Resources for Parents and Caregivers – Administration for Children and Families
- Parenting while coping with depression
- Resilience topic landing page and resources – American Psychological Association
- Taking care of ourselves – Activities for parents (English)
- Taking care of ourselves – Activities for parents (Spanish)
- Checking your employee benefits for Employee Assistance Programs, which typically include mental health support.
Mindfulness Tips:
- Check your employee benefits for subscriptions to paid mindfulness and meditation services, such as Calm or Chill Anywhere.
- Search your phone’s app store for apps that offer free services.
- Youtube is a great resource for finding free mindfulness and/or meditation sessions of any length.
More Like This
Activities and experiences play a vital role in shaping a child’s mental health and well-being. Our mental health expert, Michael Gouterman, shares how to create a positive mindset in your child through everyday activities.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
Here are some simple yet powerful activities that can cultivate positive mental health experiences:
- Establishing Rituals and Routines
Rituals and routines provide a sense of predictability and stability for young children, helping them feel safe and secure in their environment. Consider incorporating the following rituals and routines into your daily life:- Morning and bedtime routines: Establish consistent rituals for waking up and going to bed, such as reading a bedtime story or sharing highlights from the day.
- Mealtime rituals: Create special traditions around mealtime, such as setting the table together or sharing a favorite family recipe.
- Transition rituals: Develop rituals for transitions, such as saying goodbye before leaving for school or welcoming your child home after a day apart. Don’t be afraid to be creative and make your own unique rituals as a family.
By consistently practicing these rituals and routines, you can instill a sense of familiarity and connection in your child’s daily life, promoting a feeling of safety and predictability.
- Exploring New Experiences
While routines provide a sense of security, it’s also important to expose children to new experiences and challenges to support their growth and development. Here are some ways to encourage exploration and curiosity:- Visit new places: Take your child on outings to explore new environments, such as parks, museums or community events. There are many opportunities each month to gain free access to many of the popular museums and attractions throughout the Chicagoland area.
- Try new activities: Encourage your child to try new hobbies or activities that spark their interest, whether it’s painting, dancing or playing a musical instrument.
- Embrace nature: Spend time outdoors exploring nature together, whether it’s going for a hike, collecting and sorting leaves or playing in the backyard.
By introducing new experiences in a supportive and encouraging environment, you can help your child develop confidence, resilience and a sense of curiosity about the world around them.
- Cultivating Connection
Building strong connections with caregivers, family members and peers is essential for promoting positive mental health in early childhood. Here are some ways to foster meaningful connections:- Quality time: Set aside dedicated time each day to spend one-on-one with your child, engaging in activities they enjoy and showing genuine interest in their thoughts and feelings. Even for the busiest of schedules, dedicating a small amount time together can have a tremendous impact.
- Family traditions: Create special traditions and rituals that bring your family together, such as movie nights, game nights or weekend outings.
- Social interactions: Encourage your child to interact with peers through playdates, preschool or community groups, providing opportunities for friendship and social development.
More Like This
Mental health is a vital aspect of our overall well-being and serves as a strong base to navigate the ebbs and flows of our day to day lives with resiliency. But what exactly is mental health, and why is it so important in early childhood development? Our mental health expert, Michael Gouterman, shares his expert insight on understanding mental health in early childhood.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
What is mental health?
At its core, mental health encompasses social, emotional, and psychological well-being. It’s about how we think, feel, and behave, and how we navigate the world around us.
Providing safe environments for children, where they can build relationships and connections with their caregivers and loved ones, has a positive impact on their mental health. These early interactions lay the groundwork for a child to learn and feel a sense of safety and security in the world.
In these safe and nurturing environments, children begin to develop what psychologists refer to as a secure attachment which Influences how children relate to others throughout their lives.
Why is mental health important in early childhood development?
At Start Early, we know that the foundation of a child’s social and emotional competence begins forming in the prenatal relationship and continues to be laid the very first days, months, and years of life, shaped by the interactions babies have with their parents and other caring adults. Babies thrive when they are securely attached to someone special—their mother, father or other primary caregiver—who knows and responds consistently and reliably to their needs.
Mental health is a lifelong journey that is shaped by our experiences, relationships and environments. We know from research that quality programs for infants, toddlers and their families can make a significant impact on their lives, a difference that can last a lifetime.
As we embark on this journey of exploration and understanding, let’s remember that mental health is not a destination but a continuum. By nurturing our own mental well-being and supporting those around us, we have the opportunity to build a stronger world for everyone to thrive as their best selves.
More Like This
The earlier that we can start to help our children understand their emotions, the better the outcome in raising kind, empathetic children. Brain scientists, educators, economists and public health experts all agree that building a good foundation for healthy relationships begins at birth. The earlier that your child can adapt and develop key social-emotional skills—like attentiveness, persistence and impulse control—the sooner they can begin engaging in healthy social interactions with peers.
Young children aren’t necessarily born with the skills to engage in healthy relationships; they are born with the potential to develop them. With young children, it’s important that parents teach empathy by being the example. Show empathy daily to your children, family, and others in your community during your day. When empathy is shown by the parent, talk that through with your child by being attentive to their feelings. Use language like “I know that was hard for you, you seemed sad but you’re safe and loved.” This language will help children to be aware of their own emotions and feelings, in turn helping them be empathic to others.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
Tips for Parents:
- Explore your child’s emotions together and engage them in imaginative play to learn how to express those feelings so that they can better manage their emotions before starting preschool.
- Teach your child that it’s okay to have whatever feeling they are having: anger, frustration, embarrassment, fear, even rage, but that it is not acceptable for their actions to cross over and affect someone else negatively.
- Teach your child that it’s good to try to understand why someone else is having negative feelings. There may be a very good reason for their friend or acquaintance to be feeling angry or afraid.
- Teach your child that it’s never okay for them or anyone else to use their feelings as an excuse to verbally attack someone. And that when someone does this, it is time to get an adult into the situation.
You as a parent play an important role along with your child’s teachers in laying a strong foundation for social-emotional skills that will help your child to form healthy relationships. It is important for the adults in your child’s life to model positive behaviors and set clear rules.
Activities
Here are 2 activities that you can do at home with your little one to help teach them about empathy:

Make a Kindness Tree
The Kindness Tree is a symbolic way to record kind and helpful actions. Family members place leaves or notes on the tree to represent kind and helpful acts. Parents can notice these acts by saying, “You __(describe the action)__ so __(describe how it impacted others)__. That was helpful/kind!” For example, “Shubert helped Sophie get dressed so we would be on time for our library playdate. That was helpful!”
The Kindness Tree can also grow with families who have children of mixed ages. Initially, young children simply put a leaf on the tree to represent kind and helpful acts. As children grow and learn to write, the ritual evolves to include writing the kind acts down on leaves or sticky notes. Start your own Kindness Tree with this template.
Families with older children can simply use a Kindness Notebook to record kind acts and read them aloud daily or weekly.
Make a We Care Center
 The We Care Center provides a way for family members to express caring and empathy for others. Fill your We Care Center with supplies like minor first aid items (Band-Aids, wet wipes, hand sanitizer, scented lotion), card-making supplies (preprinted cards, paper, crayons, sentence starters), and a tiny stuffed animal for cuddling.
The We Care Center provides a way for family members to express caring and empathy for others. Fill your We Care Center with supplies like minor first aid items (Band-Aids, wet wipes, hand sanitizer, scented lotion), card-making supplies (preprinted cards, paper, crayons, sentence starters), and a tiny stuffed animal for cuddling.
When a friend or family member is ill, hurt, or having a hard time, your family can go to the We Care Basket to find a way to show that person they care. At first, parents might need to suggest how and when to use the We Care Center, but your children will quickly understand the intent. In this way, the We Care Center encourages the development of empathy by providing a means for children to offer caring and thoughtfulness to others every day.
This content was cross-promoted on our partner’s website, Big Heart World. Check out Big Heart World for additional social-emotional resources for parents and educators.
More Like This
For over 40 years Start Early has worked tirelessly to advance quality early learning and support for children and families. We know that starting early has the biggest impact on a child’s development and that Head Start and Early Head Start are an essential part of our work to help all children thrive.
In honor of Head Start Awareness Month, we spoke with Diana McClarien, our vice president of the Early/Head Start Network, to share how our relationship with Head Start began, the benefits of the program and our hopes for the future of Head Start and Early Head Start.
Invest in a Child’s Earliest Years
The first five years are a critical window to shape lifelong success. Act now to ensure children have the best start in life through quality early learning.
Start Early & Head Start
 Start Early’s partnership with Head Start began in 1985, coinciding with the launch of the Beethoven Project, a groundbreaking program developed to provide wraparound services – including early education options – to families in Chicago’s Grand Boulevard neighborhood. Initially starting off as a grantee of Head Start funding, Start Early has since developed a deep, decades-long relationship with Head Start, that has culminated in a Start Early, Early/Head Start Network, two directly operated programs, and the aligned goals of delivering equitable access to high-quality early learning and care for children and families in the areas in which we operate.
Start Early’s partnership with Head Start began in 1985, coinciding with the launch of the Beethoven Project, a groundbreaking program developed to provide wraparound services – including early education options – to families in Chicago’s Grand Boulevard neighborhood. Initially starting off as a grantee of Head Start funding, Start Early has since developed a deep, decades-long relationship with Head Start, that has culminated in a Start Early, Early/Head Start Network, two directly operated programs, and the aligned goals of delivering equitable access to high-quality early learning and care for children and families in the areas in which we operate.
As our network now stands, we partner closely with several local community-based agencies, including our two directly operated programs – Educare Chicago and Healthy Parents & Babies – delivering not only early learning services but also crucial components like doula, home visiting, nutrition, family, health and wellness services. With Black and Hispanic children representing a disproportionate share of children living in disinvested areas, Head Start programs also play a crucial role in addressing opportunity gaps in school readiness for children facing systemic barriers.
Looking to the future, we will continue working in tandem with Head Start to best meet the needs of the families we serve and continue centering family and early childhood education provider voices and expertise in all areas of our work. We are also working to expand our network reach by partnering with new agencies to deliver Head Start services throughout Chicago and our surrounding suburbs and are actively expanding our efforts to address the teaching shortage in the early education field. Through this approach, we hope we can continue providing the best-in-class early education and services so that our children and families within our communities and programs can thrive.
In the 2022-2023 school year, Start Early served over 1,900 people through Head Start & Early Head Start programs, including 39 pregnant women.
Head Start 101
Learn more about Head Start’s crucial role in promoting early childhood education, school readiness and comprehensive support for children and families across the country.
What is Head Start?
Head Start (HS) is a nation-wide, federally funded compensatory preschool education program. Head Start and Early Head Start (a division of Head Start specifically focused on children aged zero to three) are designed to promote school readiness in infants, toddlers and preschoolers. Head Start also serves pregnant women with a range of prenatal supports and postpartum educational opportunities.
Since 1965, Head Start has long been considered a premier model for early childhood programs (Ramey & Ramey, 2010), and has aimed to foster development and school readiness skills for children from primarily low-income communities.
With Black and Hispanic children representing a disproportionate share of children in poverty, Head Start programs act as a lever to address longstanding racial and ethnic gaps in school readiness outcomes.
Children that participate in Head Start programs make tremendous progress in the areas of language, literacy, and math, and achieve average scores related to letter-word knowledge by the end of their first year (Aikens et al., 2013; Bloom and Weiland, 2015).
The benefits are even more robust for children enrolled in Early Head Start, with higher kindergarten readiness scores and increased social-emotional, language, and cognitive development than children who never attend a Head Start program. (Love et al., 2002)
Head Start as a Model
Head Start programs are typically located in high-poverty areas and provide comprehensive services that address the needs of the whole child, including their physical, social, emotional, and cognitive development.
Many Head Start and Early Head Start programs are located within nonprofit organizations. These nonprofit organizations are uniquely positioned to help identify child care needs and develop workable solutions for families. They can also connect families with additional services through their network of local partners, who are able to leverage alternative sources of funding.
Invest in a Child’s Earliest Years
The first five years are a critical window to shape lifelong success. Act now to ensure children have the best start in life through quality early learning.
Celebrating Head Start Awareness Month
As part of Head Start Awareness Month, our Early/Head Start Network will launch a Child Development Associate® (CDA) program for parents that have children in Start Early and partner sites. The CDA Credential™ is an important credential for early childhood professionals, as obtaining it allows them to take the next step in their career.
We hope to engage with Head Start parents everywhere to elevate their perspectives and gain insights on the best ways to support their children. We know that when teachers and parents are aligned in building a solid foundation, children can thrive.
Join us this October as we celebrate and promote Head Start on social media! Use the #HeadStartAwareness hashtag in your posts to highlight the program.
More Like This
Citations
- Bloom, H. S. and Weiland, C., Quantifying Variation in Head Start Effects on Young Children’s Cognitive and Socio-Emotional Skills Using Data from the National Head Start Impact Study (March 31, 2015).
- Love, J. M., Kisker, E. E., Ross, C. M., Schochet, P. Z., Brooks-Gunn, J., Paulsell, D., Boller, K., Constantine, J., Vogel, C., Sidle Fuligni, A., Brady-Smith, C. (2002). Making a difference in the lives of infants and toddlers and their families: The impacts of early Head Start. Volumes I-III: Final technical report and appendixes and local contributions to understanding the programs and their impacts. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation.
Please join me in celebrating the release of Flourishing Children, Healthy Communities, and a Stronger Nation: The U.S. Early Years Climate Action Plan. Since its launch in June 2023, it has been my honor to serve as Co-Chair of the U.S. Early Years Climate Action Task Force, and I am grateful to my fellow Task Force members for their contributions and to Capita and the Aspen Institute for creating a forum for this important work. We owe the success of these recommendations not only to their hard work but also to the insights that were so generously shared with us by caregivers and other early childhood, health, climate and systems leaders through listening sessions.
Start Early believes that our early childhood system should be high-quality, equitable and responsive—and climate-resilient. Adapting and expanding our child- and family-facing services in the years ahead is especially critical to our ability to support those most impacted by climate disruption: pregnant people, infants, and young children, particularly those with disabilities and those impacted by environmental injustice and racism in America.
Together, the early childhood and climate change mitigation fields must look to the strengths and protective factors offered by our early childhood system to support these high-priority populations in the context of a changing climate. The challenge of climate change is daunting, but well-resourced, accessible early childhood systems are key in helping young children and their caregivers prepare and adapt. Child- and family-serving programs are key resources in both helping children and their families remain safe amid climate emergencies and helping them prepare for the future of our changed climate by building resilience, navigating information and resources and strengthening community networks.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive noteworthy developments in state and federal early childhood news, policy trends and stories highlighting work across our network.
As you review the Task Force’s recommendations, I hope you’ll take them as both a call to action and an invitation for partnership. The actions proposed for policymakers; federal, state, and local systems change leaders; funders; and researchers can only be meaningfully implemented in true partnership with the families and early care and learning providers. As we collectively face the daunting challenges associated with climate change, our policies and resiliency planning efforts must be rooted in bidirectional relationships with caregivers of young children; we must center their voices and experiences and collaboratively develop solutions that work.
The parents and caregivers who shared their experiences with us made it clear: even as coordinated, systems-level solutions begin to emerge, parents and providers have already been innovating and identifying their own solutions to keeping pregnant people, infants, and young children safe and happy in a changing climate. Let’s partner with them to advance these innovations and move forward together to co-design a more climate resilient future for our nation’s families, expectant parents and youngest children.
Why is it so important to ensure that children have quality care and educational experiences in the earliest years of life? A nurturing and supportive environment during a child’s first years lays the foundation for future success in school and life. To truly appreciate why this time of life is so crucial, it helps to understand a little bit about brain science and early brain development.
The First Years of Life: What does science tell us?
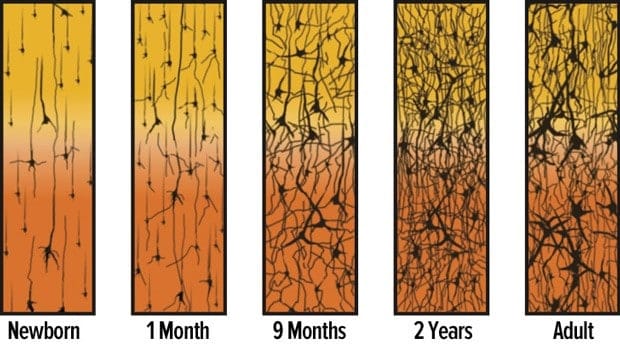
During the first several years of a child’s life, the brain forms over one million neural connections every second.
Babies’ brains are quite literally wired to learn. This rapid absorption of information creates new neural connections and builds the architecture of a baby’s brain. For comparison, adult brains have thicker, but fewer, synaptic connections.
This makes adults more efficient at doing what they’ve done before (e.g., speaking, writing and reading) but less effective at learning new things, such as a foreign language.
Original source: Adapted from Corel, JL. The postnatal development of the human cerebral cortex. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1975. Link source: Urban Child Institute
The above figure illustrates the rapid rate at which synapses are formed in the first few years of life. One can see that adults have thicker, but fewer synaptic connections.
Everything in a child’s environment — experiences, relationships with parents and caregivers and environmental factors — influences brain development and growth.
It is no surprise, then, that early experiences have a profound impact on a child’s future ability to succeed in school, work and life.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
The Importance of Early Interventions
Secure and nurturing early childhood experiences form strong neural connections, which enable children to acquire language and communication skills, learn how to interact with people and their surroundings, and develop the ability to regulate their emotions.
Sadly, too many children — especially those living in under-resourced communities — face chronic stress and adversity which hinder their ability to learn and increase their chances of falling behind developmentally and academically for years to come. Fortunately, there’s a wide body of research that demonstrates that interventions, particularly in the first years of life, make a difference.
Studies on high-quality, comprehensive early childhood programs, such as the Carolina Abecedarian Project, the Perry Preschool Project, the Chicago Child-Parent Centers, as well as Educare schools, demonstrate that early childhood interventions promote positive results in emotional development, school readiness, academic achievement and family life.
As part of our effort to become the country’s most trusted resource for early childhood knowledge Start Early conducts research with the overarching goal of generating new knowledge and contributing to the field’s understanding of how to improve the quality of programs and systems, promote positive outcomes, and transform practices and policies at scale.
Amanda Stein, director of research & evaluation
How does the science on brain development influence our research on early interventions?
The research conducted at Start Early is anchored by science. Building upon decades of studies on brain development and early childhood education, we conduct high-quality research and help translate this research into practice — with the goal of improving outcomes for children and families early in life.
One example of how our research comes to life is demonstrated by the work of Educare schools. Start Early opened the first Educare school in 2000 on Chicago’s South Side using a research-based curriculum and serving low-income infants, toddlers, preschoolers and their families. Now part of a nationwide network of 25 schools, known as the Educare Learning Network, these schools are prime examples of the positive outcomes stemming from high-quality early education programs.
After just one year at an Educare school, children show improved language skills, fewer problem behaviors, and more positive interactions with parents. Children who enrolled in Educare schools earlier, and stayed until they entered kindergarten, also displayed stronger vocabulary skills — just one of many positive indicators of effective early intervention. Years of rigorous evaluations of Educare programs indicate these outcomes.
Yet, Educare is just one example of how existing science and our own rigorous research join to create and promote high-quality early learning experiences. Ultimately, our research aims to reinforce the existing evidence supporting the importance of early education, while also informing and advancing improvements in the field as a whole.
There’s been a national discussion about increasing our aptitude in the fields of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM)/science technology, engineering, arts and math (STEAM). America is underperforming other industrial nations, and these areas are increasingly playing a critical role in career success.
Much of the conversation focuses on improvements in the middle and high school years. But we can begin building STEM/STEAM skills much earlier than that—as soon as a child starts speaking.
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.
Some young children are innately interested in: learning how things work, building things and taking things apart. But all children can be enticed into STEM/STEAM learning through whatever they’re already interested in. Both STEM and STEAM support play, wonder and curiosity; but STEAM includes an art component that allows children to create and design with intention. STEM and STEAM encourage children to solve problems by using inquiry and investigation.
Since young children tend to ask lots of questions, you can introduce STEM/STEAM basics by following these simple “CHIA” steps:
- Curiosity: “So glad you asked!”
- Hypothesis: “Why don’t you make a guess?”
- Investigation: “Let’s look into it!”
- Analysis: “Why do you think that happened?”
Before beginning any activity with your toddler, ask them what they think is going to happen. Then ask why they think that. They’ve just created a hypothesis and given their logic for that hypothesis—the foundation of all scientific exploration. By then creating experiments with your toddler and talking about what you observe, you’re setting them up to plan, brainstorm, build, and solve problems exactly like scientists and engineers do.
Ideas for You and Your Child:
- Build a ramp for toy cars to roll down. Have your toddler race two cars down the ramp. Ask them to predict which one will get to the bottom first. Then have them play with how to make the cars faster or slower. For example, if you put a small stone on the car, does it make it go faster? Buildable toys provide great opportunities for experimentation. What happens to the speed when your toddler makes the car bigger, heavier, or longer? This is experimentation, and it’s fun!
- When you go for a walk, you can guide the conversation, or let your child come up with their own experiments. If you see an animal, play with how softly you can talk before the animal notices you. Or ask your child why the squirrels race around the tree. Right answers are not the goal—this is about asking questions and predicting the answer.
Remember that it’s okay for both you and your child to answer “I don’t know” to any question. It’s asking the question that’s important because that is where all science begins.
STEAM At-Home Activity: Building Structures
While at home, parents can introduce building structures with their children. The materials for this activity consist of wide popsicle sticks, clear plastic drinking cups and small cube blocks. Parents can encourage their child to build a structure while engaging in conversation about how many cups will it take to build the structure. What will happen if you use fewer cups and more popsicle sticks? How high can you build? The children can learn about balance, height, measurement and a host of wonderful things. This at-home activity needs little to no planning, but a readiness to think outside of the box.
Don’t underestimate the incredible thinking skills that young children have. With just a playful shift in word choice, we can allow for a dramatic shift in getting our babies ready for a STEM/STEAM education!
More Like This
Stay Connected
Sign up to receive news, helpful tools and learn about how you can help our youngest learners.