
Notes From Olympia: Feb. 2, Week 4 of the 2024 Legislative Session
This edition includes highlights from legislative week 4, policy committee cutoff deadlines and details, updates on early learning related bills, Washington State Capitol trivia and much more.
 The Tivoli Fountain Replica is showing off on a sunny Tuesday (the original Tivoli Fountain is in Copenhagen!)
The Tivoli Fountain Replica is showing off on a sunny Tuesday (the original Tivoli Fountain is in Copenhagen!)
(Photo Credit: Zoë Erb)
Trivia
The Winged Victory Monument on the Northeast side of the Capitol campus pays tribute to what group of individuals?
Week 4 Highlights
Dairy Day!
In years past, I have written about the joy brought to the Capitol campus on the “food days” sponsored by various food associations. Not only has January been a long and rainy month, but it has also been devoid of any free food days.
Thankfully, our dark days ended Feb. 1 when the Washington State Dairy Federation sponsored “Dairy Day.” The kind folks at the Dairy Federation shared a variety of offerings ranging from yogurt to cheeses to numerous ice cream options. I cannot think of a better way to turn a post-policy committee cutoff frown upside down than free ice cream!
Policy Committee Cutoff
Wednesday marked the first milestone of the 2024 short session with the House of Origin policy committee cutoff. Bills that did not pass out of policy committee by this deadline are considered “dormant” (a more strength-based term than “dead” that I’ve picked up to describe bills that are not advancing). Many policy committees held jam-packed hearings this week to hear, amend and vote upon the many bills before the Legislature this short session.
Some other items of note:
- This is a particularly important time to keep an eye on adopted amendments or substitutes as the focus of bills can change on a dime. It is not unusual to see the scope of legislation shift to keep a bill moving, or scaled back to minimize cost, for example. I will note a couple of examples below where amendments significantly shifted the focus of a bill.
- “This bill’s a mover!” It is not uncommon for “companion” bills to be introduced (identical bills in the Senate and the House) on a specific issue. These companions provide an opportunity for an idea to be socialized in both chambers with the intention of increasing the likelihood of its passage. As time becomes scarcer as the session progresses, it is typical for one of the vehicles to be identified as the “mover,” and the other bill to go dormant. An example of companion bills where a mover has been identified is HB 2111 (Nance), a technical clean-up bill related to Working Connections Child Care statute. In this case, HB 2111 is the mover, and its companion, SB 5941 is dormant. If you are advocating or speaking to certain bills, it is helpful to double check you have the “mover” identified.
We have adjusted our bill tracker on our state policy resources page to reflect the bills advancing at this point of session. We moved the “dormant” bills to a separate chart to make it easier to identify the smaller group of active bills.
A Recap of Bill Activity
Fentanyl/Opioid Crisis and Family Supports
A primary focus this legislative session has been the impacts of the national fentanyl/opioid crisis on families. Two pieces of legislation – SB 6109 (Sen. C. Wilson and Boehnke) and HB 2447 (Rep. Senn) are the primary vehicles for conversations around fentanyl and child removal standards as well as the need for additional services and supports for families experiencing substance use disorder.
The first sections of both bills look to address what level of consideration should be given to the risks of fentanyl in decisions about whether a child should remain in the home of a parent. These are weighty and critical decisions as lawmakers aim to balance keeping children safe while avoiding unnecessary family separation. Expect these discussions to continue as lawmakers continue to grapple with this important decision.
Both bills contain “services and supports” for families in the second sections. Although these services and supports are not in complete alignment, they are very similar. For example, both bills:
- Expand inpatient substance use disorder treatment beds to include family-centered treatment where children can remain with their parent(s).
- Provide contracted child care slots for infants engaged in child protective services.
- Launch contracted, targeted home visiting slots for families experiencing substance use disorder.
Additionally, both bills look to leverage the skills and expertise of public health nurses by connecting them with families to provide education on the risks of high-potency synthetic opioids and child health and safety practices. Further, the House bill contains a provision to fund a pilot project in two communities for Promotoras to provide culturally sensitive, lay health education for the Latinx community and act as liaisons between their community, health professionals and human and social service organizations.
The Senate Ways and Means Committee heard SB 6109 Jan. 29 and, of this writing, it has not been scheduled for an Executive Session. The House Human Services, Youth and Early Learning Committee passed HB 2447 Jan. 30 and it has been referred to the House Appropriations Committee.
Non-Standard Hour Child Care
The Senate Ways and Means Committee is scheduled to hear SB 6171 (Sen. L. Wilson) Feb. 3. I highlight this bill as an example of one that underwent a significant change in its policy committee.
As introduced, the bill would have called for a study on child care for criminal justice personnel. The Senate Human Services Committee did not consider the original bill, but instead heard and passed a substitute bill which calls for DCYF to conduct a feasibility study and provide cost estimates for a pilot program to award start-up grants in jurisdictions with over 100,000 people to assist with establishing and operating child care programs and services with nonstandard hours for the minor children of individuals in high demand professions including, but not limited to, peace officers and criminal justice personnel, firefighters, medical professionals in rural areas, and construction workers during shift work and abnormal work hours.
Department of Children, Youth and Families Oversight Board
HB 2185 (Reps. Dent and Senn) is scheduled to be heard in the House Appropriations Committee Feb. 2, with an Executive Session (or vote) scheduled for Feb. 5.
This bill is designed to make changes to the make-up and charge of the Department of Children, Youth and Families (DCYF) Oversight Board. This is another bill that experienced changes from its introduction after review in the House Human Services, Youth and Early Learning Committee.
Among other provisions, the substitute maintains the transfer of authority for the Oversight Board from the Governor’s Office to the Legislature, makes further modifications to the Oversight Board’s membership and removes the authority of the Oversight Board to overturn, change, or uphold decisions made by (DCYF) licensors regarding adverse child care licensing decisions not involving a violation of health and safety standards.
What’s On Deck Next Week
As the great philosopher Ferris Bueller once said, “Life moves pretty fast. If you don’t stop and look around once in a while, you could miss it.” I’m not sure if there’s an apt analogy there, but the legislative session does move darn fast. Especially in a short session.
Fiscal Committee Cutoff and then Floor Session!
By the time you receive the next Notes from Olympia, we will have already made it through the fiscal committee cutoff of Feb. 5 and will be knee deep in legislative Floor activity. To prepare for this fiscal cutoff, legislative fiscal committees (primarily the Senate Ways and Means and House Appropriations Committees) will have considered all bills with a fiscal impact. Expect many of the bills that do make it out of these fiscal committees to be amended to include language conditioning their implementation on funding being provided in the supplemental budget, or “subject to appropriation.”
The next big cutoff is the House of Origin Floor cutoff Feb. 13 and that is when all bills must pass out of their house of origin. This is a particularly stressful time for advocates because, unlike policy and fiscal committees, no calendars announcing meeting times or agendas are available. This requires a lot of waiting around on the third floor of the Legislative Building, trying to track down any tidbits of information.
During Floor activity, “clock time” is a strategy often deployed by the minority party who may not want to see bills passed, so they might offer up voluminous amendments or designate a number of their caucus members to speak to bills, all to eat up time. This influences the majority party’s strategy of scheduling bills for a Floor vote. If they schedule too many controversial bills, that will limit the time available for other important bills.
We will see how it plays out this year, but I’m confident in saying that folks in all corners of the Legislative Building will be tired and grumpy during the period of Floor activity!
What is NTIB?
The initials NTIB look like they are part of a National Transportation agency, but it is a very important term to the Washington state legislative process that means “Necessary to Implement the Budget.”
Like the English language, the legislative process has exceptions to its rules. Bills deemed Necessary to Implement the Budget (or NTIB) are exempt from the cutoff deadlines due to budgetary impacts. These bills still must go through each of the steps – they must, for example, receive a Floor vote (no skipping steps!). NTIB status is granted by legislative leadership and is not broadly given. Typically, bills that are NTIB are ones that are more controversial and/or under negotiation.
Bill Tracker
Our bill tracker is updated each Thursday and linked on our policy resources page. Because bills move quickly, the tracker may not have the most recent updates, but this information can be found on the legislative website.
Trivia Answer
 The sun shines on Nike and her entourage
The sun shines on Nike and her entourage
(Photo Credit: Zoë Erb)
Winged Victory, or Nike (νίκη being the official Greek name), pays homage to the 67,106 Washingtonians who served during World War I, including the more than 1,600 soldiers who died during the war.
The figures surrounding Nike represent members of the Navy, the Army, the Marines and a Red Cross nurse. Governor Ernest Lister proposed the statue’s creation in 1919 and the Legislature allocated $50,000 for its construction (equivalent to about $900,000 today). It turned out this was not enough funding and the total cost ended up closer to $100,000, funded by federal grants and through the sale of state lands.
Winged Victory has been standing on the northeast side of the legislative building at the Capitol since its dedication May 30, 1938. Sculpted in bronze, the 12-foot statue sits on top of a 10-foot granite base. Its sculptor, Alonzo Victor Lewis, was subsequently named Washington Sculptor Laureate by the State Legislature.
Notably, Nike holds an olive branch in her right hand, usually symbolizing peace. The ancient Greeks and Romans also associated it with supplication—praying for something from the gods (whether it be peace, prosperity, etc.).
The inscriptions on the modern, Washington State Nike are as follows:
- East face: the WA State Seal, “To the memory of the citizens of the State of Washington who lost their lives in the service of the United States during the World War 1917 – 1918.”
- North face: “Greater love hath no man than this, that a man lay down his life for his friend.”
- West face: “Their sacrifice was to vindicate the principles of peace and justice in the life of the world.”
- South face: “They fought to safeguard and transmit to posterity the principles of justice, freedom, and democracy.”
In addition to the statue of Nike, Washington State’s Capitol Campus includes memorials for those who served in World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, as well as those who received Prisoner of War/Missing in Action and Congressional Medals of Honor.
According to the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, at least 12 other states also have statues dedicated to war veterans on their capital campus, including: Arizona, California, Florida, Louisiana, Minnesota, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Texas, Utah and West Virginia. If you’re curious to learn more about these statues, each state has its own veteran’s affairs page with more information.
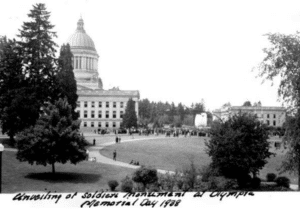 Postcard of “Winged Victory” Unveiling: 1938
Postcard of “Winged Victory” Unveiling: 1938
(Photo Courtesy: Washington State Archives)
Resources:
Winged Victory Monument [WA State Department of Enterprise Services]
Winged Victory [olympiahistory.com]
Winged Victory Monument (WWI) [The Clio]
At the state Capitol, a longstanding tribute to lives lost in WWI [WA State Standard]
Veteran’s Memorials on Capitol Campus [WA State Legislature]
Popular State Veteran Monuments [US Department of Veteran Affairs]
About the Author

Erica Hallock
Director, Policy & Advocacy, Start Early Washington
Erica Hallock serves as the Director of Policy and Advocacy for Start Early Washington. She has worked in early childhood, health and human services policy in both California and Washington state.
More Like This
Contact Us
Connect with our team to learn more about our work or discuss how we can support policy and advocacy work for your organization.
Washington State Hub
Learn more about our work in Washington state and access relevant resources and publications.
